Breathe to Heal: A simple Guide to Restoring Your Mind & Body
- healingsoulacuherb
- Nov 14, 2025
- 3 min read

Breathing is one of the most crucial activities for generating and circulating energy (qi) in the body. In traditional medicine, breathing goes beyond merely supplying oxygen—it plays a fundamental role in creating and moving qi throughout the organs and meridians, which is essential for maintaining health.
THE IMPORTANCE OF BREATHING
Breathing balances yin and yang. Exhaling is associated with yang, while inhaling relates to yin. When we exhale, we release unnecessary energy (such as heat or carbon dioxide), and when we inhale, we bring in fresh oxygen and vitality. If this process is not functioning smoothly, tension and discomfort can build up in the body, leading to various health problems.
Particularly when we’re angry or stressed, our heart rate increases, and the body’s tension levels spike as the sympathetic nervous system becomes activated. At times like these, it’s important to breathe deeply and slowly. Simply taking deep breaths and exhaling slowly can greatly reduce tension and help calm your emotions.
PROPER BREATHING TECHNIQUES
1. Deep Breathing: Start by lightly inhaling and then exhaling deeply. Inhale for three seconds, then exhale for six seconds. Repeating this process six times can significantly reduce tension in the body.
2. Diaphragmatic Breathing (Abdominal Breathing): The focus is on breathing deeply using the diaphragm. The primary goal is to move the air deeply into the lungs, expanding the lower abdomen as you inhale. Inhale through the nose, allowing the belly to rise, and exhale through the mouth, allowing the belly to fall. This promotes deep relaxation and reduces stress by activating the parasympathetic nervous system. This method is typically used for calming the body and mind, improving lung function, and promoting relaxation.
3. Hypogastric Breathing (Danjeon Breathing): The focus is on gathering and circulating energy (qi or chi) in the Danjeon, a point about 2-3 inches below the navel. Similar to diaphragmatic breathing, but with a stronger emphasis on controlling and directing the breath towards the Danjeon area. Practitioners visualize energy being stored in this area as they breathe. This breathing technique is not just for relaxation but for cultivating internal energy, balancing the body’s qi, and improving vitality. It is often used in martial arts, meditation, and traditional Eastern practices.
4. Maintaining a Rhythm: Keeping a steady rhythm in your breathing is essential. Calm and steady breathing helps maintain the body’s balance and circulation. Deep, slow breaths are beneficial, while shallow and fast breathing can lead to tension, so it’s best to avoid it.
BEGINNER IN DIAPHRAGMATIC (ABDOMINAL) BREATHING:
When you first begin diaphragmatic breathing, it's recommended to practice while lying down.
1. Lie on your back with your knees bent at about a 90-degree angle.
2. Place your feet shoulder-width apart and rest your hands beside your hips.
3. Inhale deeply through your nose for 3 seconds, letting your belly expand fully.
4. Hold your breath for 3 seconds, then exhale slowly through your mouth for 6 seconds, drawing your belly button towards your spine.
5. Repeat steps 1-3 ten times for five sets.
• Abdominal Breathing - Inhale

• Abdominal Breathing - Exhale

BREATHING & QI CIRCULATION
In traditional Korean medicine, breathing is referred to as “Cheong-qi”, which signifies the “clear qi.” It is considered a fundamental source of vital energy, or “qi,” in the body. Qi helps circulate blood, makes the heart beat, and ensures the proper functioning of all organs and tissues. Additionally, qi is closely linked to emotions, meaning that we can regulate the flow of qi through breathing when faced with stress or emotional changes.
In essence, breathing generates and circulates qi, which keeps the body healthy and prevents diseases. By practicing proper breathing techniques, you can maintain balance in the body, ensuring that your qi flows smoothly and that both your body and mind remain in good health.
Therefore, regularly practicing deep and abdominal breathing to regulate your qi is essential for maintaining overall well-being.
UNERSTANDING ABDOMINAL & DANJEON BRATHING
Here’s a visual guide to help you easily understand the difference between abdominal breathing and danjeon(lower abdominal) breathing. Review the details below and practice the proper breathing technique.
• Abdominal Breathing - Inhale
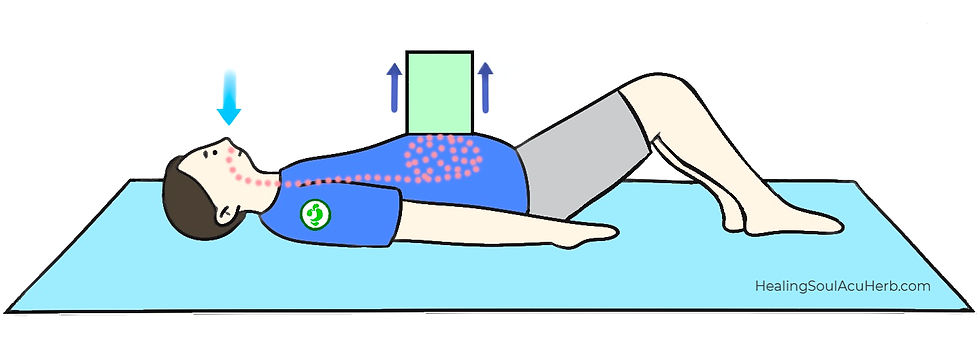
• Danjeon(Lower Abdominal) Breathing - Exhale

___________________________________________________________________
*If you want to restore balance to your mind and body, please reach out to us!
Healing Soul Acupuncture & Herbal Clinic
301-433-9150



Comments